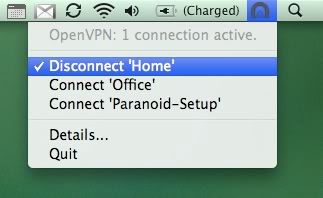
Langkah 1
Ok. Coba deh dowload source tunnelblick di : (gratis kok)
http://code.google.com/p/tunnelblick/
dan install… drag aja tunnelblick ke folder applications
Langkah 2
Cara settings tunnelblick
Seperti halnya viscosity atau program openVPN yang lain kita membutuhkan 3 file penting yaitu ca.cer, user.crt, dan key.key.
Simpan ketiga file penting itu di :
Users>bugemac(nama mac saya)>Library>Application Support>Tunnelblick>Configurations
Berbeda dengan viscosity, di Tunnelblick.. parameter dan setingannya tidak berupa GUI tapi berupa list perintah yang nantinya akan diload dan dieksekusi (mirip pada OpenVPN sesungguhnya).
Jadi ada satu file yang berekstensi .conf yang harus kita rubah dan diisi dengan paramater yang diperlukan. File itu ada di Users>bugemac(nama mac saya)>Library>Application Support>Tunnelblick>Configurations
Bukalah file tadi dengan textedit :
Secara default isi dari config file seperti dibawah ini. Baris yang tidak bertanda # berarti baris itu akan dieksekusi oleh tunnelblick.
##############################################
# Sample client-side OpenVPN 2.0 config file #
# for connecting to multi-client server. #
# This configuration can be used by multiple #
# clients, however each client should have #
# its own cert and key files. #
# On Windows, you might want to rename this #
# file so it has a .ovpn extension #
##############################################
# Specify that we are a client and that we
# will be pulling certain config file directives
# from the server.
# ini harus tetap ada sebab kita akan terhubung dengan vpn sebagai client
client
# Use the same setting as you are using on
# the server.
# On most systems, the VPN will not function
# unless you partially or fully disable
# the firewall for the TUN/TAP interface.
;dev tap
dev tun
# Windows needs the TAP-Win32 adapter name
# from the Network Connections panel
# if you have more than one. On XP SP2,
# you may need to disable the firewall
# for the TAP adapter.
;dev-node MyTap
# Are we connecting to a TCP or
# UDP server? Use the same setting as
# on the server.
;proto tcp
proto udp
# Port dapat dirubah sesuai dengan port dari server yang menyediakan vpn
# The hostname/IP and port of the server.
# You can have multiple remote entries
# to load balance between the servers.
remote my-server-1 1194
;remote my-server-2 1194
# Choose a random host from the remote
# list for load-balancing. Otherwise
# try hosts in the order specified.
;remote-random
# Keep trying indefinitely to resolve the
# host name of the OpenVPN server. Very useful
# on machines which are not permanently connected
# to the internet such as laptops.
resolv-retry infinite
# Most clients don't need to bind to
# a specific local port number.
nobind
# Downgrade privileges after initialization (non-Windows only)
;user nobody
;group nobody
# Try to preserve some state across restarts.
persist-key
persist-tun
# If you are connecting through an
# HTTP proxy to reach the actual OpenVPN
# server, put the proxy server/IP and
# port number here. See the man page
# if your proxy server requires
# authentication.
;http-proxy-retry # retry on connection failures
;http-proxy [proxy server] [proxy port #]
# Wireless networks often produce a lot
# of duplicate packets. Set this flag
# to silence duplicate packet warnings.
;mute-replay-warnings
# SSL/TLS parms.
# See the server config file for more
# description. It's best to use
# a separate .crt/.key file pair
# for each client. A single ca
# file can be used for all clients.
ca ca.crt
cert client.crt
key client.key
# Verify server certificate by checking
# that the certicate has the nsCertType
# field set to "server". This is an
# important precaution to protect against
# a potential attack discussed here:
# http://openvpn.net/howto.html#mitm
#
# To use this feature, you will need to generate
# your server certificates with the nsCertType
# field set to "server". The build-key-server
# script in the easy-rsa folder will do this.
;ns-cert-type server
# If a tls-auth key is used on the server
# then every client must also have the key.
;tls-auth ta.key 1
# Select a cryptographic cipher.
# If the cipher option is used on the server
# then you must also specify it here.
;cipher x
# Enable compression on the VPN link.
# Don't enable this unless it is also
# enabled in the server config file.
comp-lzo
# Set log file verbosity.
verb 3
# Silence repeating messages
;mute 20
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar